
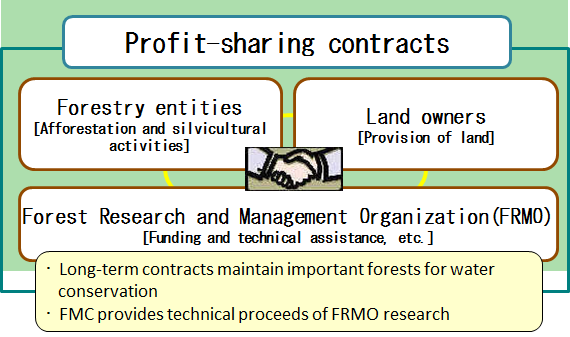
Forest Management for Headwaters
- In projects for headwaters, we have been urgently working on the management of forests as a public safety net, targeting tree-less or -dispersed land among private and protected forests in hinterland water conservation areas that are key to water conservation.
- To manage forests, we are promoting:
- Introduction of long-term rotation management making the best use of local vegetation including broad leaf trees.
- Introduction of multi-storied forest management leading to multiple crown layers
- Minimization and dispersion of cutting areas at regeneration cutting
- The total area of forests planted in projects for the forest management for headwaters is about 480,000 ha (as of the end of FY 2018), with the effective economic benefits of its public-interest function estimated at about 850 billion yen per year.
Enhancement of various forest functions
Effects on enhancement of water conservation
- Supplying of good-quality and abundant water
- Prevention of flood and Purification of water quality

Reserve about 2.9 billion m3 / year of water (equivalent to the amount of water consumed in Tokyo over two years).
Effects on environmental conservation
- Absorption of carbon dioxide
- Contribution of oxygen release and air purifying
Fixing 2.4 million tons of carbon dioxide (equivalent to the amount of CO2 discharged at power generation for electricity consumed by about 1.55 million households per year).
Effects on land conservation
- Prevention of an outflow and collapse of earth and sand
- Forest management for disaster resilience

Retaining approx. 87 million m3 / year of soil
Estimated value of various forest functions (except wood production) in project areas
Approx. 850 billion yen / year
